Muhammad Azhar Iqbal, Ishfaq Ahmad Hafiz, Nadeem Akhtar Abbasi, Muhammad AzeemTariq, Muhammad Ramzan Anser, Mahmood-ul-Hassan, Muhammad Izhar Naeem Bhatti, Muhammad Aftab, Azmat Ali Awan, and Muhammad Faisal Khan, from the different institute of the Pakistan. wrote a research article about, Olive Genotypes in Pakistan: Phenology and Pollen Assessment, entitled, Assessment of olive genotypes towards phenology, pollen viability and germination in Pakistan. This research paper published by the International Journal of Biosciences | IJB. an open access scholarly research journal on Biology, under the affiliation of the International Network For Natural Sciences | INNSpub. an open access multidisciplinary research journal publisher.
Abstract
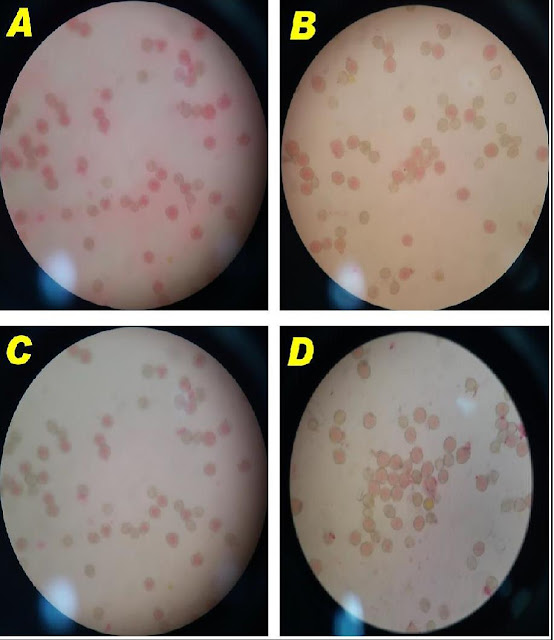
Pollen viability and
germination tests are consider key factors for final productivity. Hence
characterization of pollen and phenological aspects of eighteen olive cultivars
were studied under an experiment carried out at Barani Agricultural Research
Institute, Chakwal, Pakistan. Pollen viability was tested through Acetocarmine
and germination was analyzed in the culture media having water, boric acid,
sucrose and agar. Results depicted that the maximum number of panicles
were recorded in variety Earlik (27.90) and minimum in variety Ottobratica. In
general more number of panicles was recorded in 2018 in all most all the
varieties as compared to 2017. Highest numbers of flower per branch were
observed in variety Ottobratica in both years of study. Staminate flowers were
also noted at maximum level again in variety Ottobratica. Maximum final fruit
set percentage was recorded in variety Moraiolo (4.23 %) and Coratina (3.70 %)
in first year of study while Coratina (3.75 %) and Frantoio (3.59 %) depicted
highest fruit set percentage in second year of study. Maximum pollen viability
(79.18% & 53.08) was recorded by in Variety Gemlik while minimum values
were recorded in Variety Leccino (27.16 % & 47.62 %) in both the years 2017
& 2018 respectively. The germination rate varied among all the varieties.
Varieties Ottobratica and Gemlik showed maximum value of pollen germination
rate during the study year while minimum rate was recorded again in variety
Leccino.
Read more : Acacia nilotica_Recovery from Pesticide ExposureBark | InformativeBD
Introduction
Olive (Olea europaea L.) is an evergreen tree and prominent species of whole Mediterranean countries. Its cultivation can be traced back since ancient times and is also mentioned in the Holy Quran, Hebrew and the Christian Bibles (Flaishman et al., 2008). The olive fruit is a famous fruit tree worldwide for its oil and nutritional benefits. Successful fertilization and fruitlet persistence is directly dependent upon flower quality (Martins et al., 2006) which also predict pistil abortion rate, embrosac development, and receptivity of stigma, pollen viability and nitrogen and carbohydrate contents (Cuevas et al., 1994; Moreno-Aloaas et al., 2018). Large ovaries are associated with more fruit set. (Cuevas and Polito, 2004.) Flower quality is better in off year than on year production (Mazzeo et al., 2014). The length of inflorescence (3-8 cm) and number of inflorescence per branch and number of flower (15-30) per inflorescence varies with the cultivar (Martin and Sibbett, 2005). These characteristic may vary in each year, plant, branch, inflorescence (Brooks, 1948; Cuevas et al., 1994; Lavee et al., 1996; Lavee et al., 2002; Reale et al., 2006). The perfect or staminate flower may vary with the position of inflorescence (Bouranis et al., 1999; Dimassi et al., 1999; Ateyyeh et al., 2000; Cuevas and Polito, 2004).
Most important features in olive fruit set are self-incompatibility, self-fertility and abnormalities in morphological traits. Various factor of sterility are present in olive like more or less related species which are responsible for productivity. Olive trees with good quality and quantity of viable pollens is essential for a good pollination. As a whole, there exists a linear relation between viability and germination capacity of pollen and germination capability in many fruit species (Stanley and Linskens, 1974). Both viability and germination depends on various factors like genotype, nutrition conditions, and biotic and a biotic factors (Khan and Perveen, 2008).Poor pollen viability and germination percentage cause less fecundation in olive (Bini, 1984; Tombesi, 2013). Pollen viability is a genetic trait (Vuletin-Selak et al., 2014) and estimated by various techniques and one of the most important is staining with acetocarmine jelly (Radford et al., 1974).
Pollen germination is another important factor in olive fruit production. Growth of pollen tube in In vitro condition should be check to assess the pollen grain germination capability. Temperature and relative humidity has strong influence on pollen tube growth along with the humidity and growing media.
There is a huge difference in pollen germination on stigma in open field condition and in vitro growth (Heslop-Harrison and Heslop-Harrison, 1981; Pinney and Polito, 1990; Kovacs and Barnabas, 1997). In vitro Pollen tube germination is very sensitive to growing media. In present conditions media is considered to be suitable having water, boric acid, sucrose and agar (Pinney and Polito, 1990) and citric acid (Al-Dehadhehetal et al., 2004).
The media containing 20% sucrose is optimal and more than 30 % cause inhibition of pollen tube growth (Lavee et al., 1985). Pollen ability, germination percentage and pollination of 18 olive cultivars were evaluated. It is believed that pollen ability is an important tool for pollination process for mono orchard cultivation. Major significant differences among cultivars for pollen abilities were listed with variation in characteristic with reference to time (Shemer et al., 2014).
Olive cultivation on commercial scale has no long history in Pakistan. But during the last ten years olive plantation has gained popularity because of its great socio-economic importance. More than 4494.36 hectares have been brought under olive cultivation in Pothwar region and 2,800 acre (280,004 plants) was cultivated other than Pothwar region under Federal and provincial Government, Pakistan (PARC, 2018; BARI, 2019).
A major aim was to examine phenology, pollen viability and germinating capacity of pollens of eighteen exotic olives for identifying the most suitable genotype for newly olive industry establishment.
Reference
Al-Dehadheh AM, Ateyyeh
AF, Qrunfleh MM. 2004. Morphology, Viability,” in vitro” Germination
annAuxin Content of Pollen of Five Olive (Olea europaea L.)
Cultivars. Advances in horticultural science 18(2), 1000-1006.
Ateyyeh AF, Stosser R,
Qrunfleh M. 2000. Reproductive biology of the olive (Olea europaea L.)
cultivar ‘Nabali Baladi’. Journal of Applied Botany 74, 255-270.
Ayerza R, Sibbett GS. 2001.
Thermal adaptability of olive (Olea europaea L.) to the Arid Chaco of
Argentina. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 84(3), 277-285.
Iqbal MA, Hafiz IA,
Abbasi NA, Shah MKN. 2019. Adaptability, agronomic and yield performance
of exotic olive (olea europaea) cultivars in pothwar region of
pakistan.Pakistan journal of botany 51(5), 1-7.
BARI. 2019.
Newsletter April-June. http://barichakwal.punjab.gov.pk/
Bini G. 1984.
Flowering and pollination in olive. Studies on the pollination period, stigma
receptivity, and development of the female gametophyte. Rivista di
Ortoflorofrutticoltura Italiana 68, 57-69.
Bouranis DL, Kitsaki
CK, Chorianopoulou SN, Aivalakis G, Drossopoulos JB. 1999. Nutritional dynamics
of olive tree flowers. Journal of plant nutrition 22(2), 245-257.
Brooks RM. 1948.
Seasonal incidence of perfect and staminate olive flowers. In Proceedings
of the American Society for Horticultural Science 52,213-218.
Chagas EA, Pio R,
Chagas PC, Pasqual M, Bettiol JE. 2010. Composiçãodomeio de cultura e
condiçõesambientaisparagerminação de grãos de pólen de porta-enxertos de
pereira. Ciência Rural 40, 261-266. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S010384782010000200002.
Connor DJ, Fereres E. 2005.
The physiology of adaptation and yield expression in olive. Horticultural
Reviews 31, 155-229.
Cuevas J, Polito VS. 2004.
The role of staminate flowers in the breeding system of Olea europaea
(Oleaceae): an andromonoecious, wind‐pollinated taxon. Annals of
Botany93 (5), 547-553.
Cuevas J, Rallo L,
Rapoport HF. 1994. Crop load effects on floral quality in
olive. Scientia Horticulturae 59(2), 123-130.
Denney JO, McEachern
GR. 1983. An analysis of several climatic temperature variables dealing
with olive production. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural
Science 108, 578-581.
Dimassi K, Therios I,
Balatsos A, Metzidakis IT, Voyiatzis DG. 1999. The blooming period and
self-fruitfulness in twelve Greek and three foreign olive cultivars.
ActaHorticulturae 474, 275-278.
Fabbri A, Bartolini G,
Lambardi M, Kailis S. 2004. Olive Propagation Manual. Landlinks
Press 2, 18-23.
Flaishman MA, Yablovich
Z, Golobovich S. 2008. “Molecular breeding in fig (Ficus carica) by the
use of genetic transformation.” ActaHorticulturae 798, 151–158.
Ghrissi N. 2001.
Contribution à l’évolution agro physiologique du phénomène de
compatibilitépollinique chez l’olivier (Olea europaea L).Cas de la
collection méditerranéenne de la Menara de Marrakech. Thèse de Doctoratfaculté
des Sciences Semlalia Marrakech 85-97.
Hartmann HT, Whisler
JE. 1975. Flower production in olive as influenced by various chilling
temperature regimes. Journal American Society for Horticultural Science,
56-91.
Heslop‐Harrison J,
Heslop‐Harrison Y. 1981. The pollen‐stigma interaction in the grasses. 2.
Pollen‐tube penetration and the stigma response in Secale. Actabotanicaneerlandica 30(4), 289-307.
Jackson D, Sweet GB. 1972.
Flower initiation in temperate woody plants. New Forestry 508, 9-24.
Kartas A, Chliyeh M,
Touati J, Touhami AO, Gaboun F, Benkirane R, Douira A. 2015. Performances
and potentialities of introduced varieties and local types of olive trees (Olea
europaea L.) grown in the Ouazzane areas (North of
Morocco). International Journal of Recent Science and Research 2, 2571-2586.
Khan SA, Perveen A. 2008.
“Germination capacity of stored pollen of Ficuscarica (Moraceae) and
their maintenance,” Pakistan Journal of Botany 40(6), 2251–2254.
Kovacs G, Barnabás B. 1997.
Selection for frost tolerance in another culture-derived embryos and regeneration
of frost-tolerant fertile DH plants in winter wheat. ActaAgronomica
Hungarica 45, 285-294.
Lavee S, Rallo L,
Rapoport HF, Troncoso A. 1996. The floral biology of the olive: Effect of
flower number, type and distribution on fruitset. ScientiaHorticulturae 66, 149-158.
Lavee S, Taryan J,
Levin J, Haskal A. 2002. The significance of cross-pollination for various
olive cultivars under irrigated intensive growing conditions. Olivae 91, 25-36.
Lavee S, Harshemesh H,
Avidan N. 1985. Phenolic acids-possible involvement in regulating growth
and alternate fruiting in olive trees. In V International Symposium on
Growth Regulators in Fruit Production 179, 317-328.
Martins PC, Cordeiro
AM, Rapoport HF. 2006. Flower quality in orchards of olive, Olea europaea
L., cv. Morisca. Advances in Horticultural Science, 262-266.
Mazzeo A, Palasciano M,
Gallotta A, Camposeo S, Pacifico A, Ferrara G. 2014. Amount and quality of
pollen grains in four olive (Olea europaea L.) cultivars as affected by
‘on’and ‘off’years. ScientiaHorticulturae 170, 89-93.
Martin GC, Sibbett
GS. 2005. Botany of the olive.Olive production manual, 15-19.
Martins PC, Cordeiro
AM, Rapoport HF. 2006. Flower quality in orchards of olive, Olea
europaea L., cv. Morisca. Advances in Horticultural Science, 262-266.
Moreno-Alías I,
Trentacoste ER, Gómez-del-Campo M, Beyá-Marshall V, Rapoport HF. 2018.
Olive inflorescence and flower development as affected by irradiance received
in different positions of an east-west hedgerow. Acta Horticulture 118, 109-114.
PARC. 2018. http://parc.gov.pk/index.php/en/olive-achievements
Pinillos V, Cuevas J. 2009.
Open-pollination provides sufficient levels of cross-pollen in
spanishmonovarietal olive orchards. Horticulture Science 44(2), 499-502.
Pinney K, Polito VS. 1990.
Olive pollen storage and in vitro germination. In International Symposium on
Olive Growing 286, 207-210.
Radford AE, Dickison
WC, Massey JR, Bell CR. 1974. Vascular plant systematics. New York:
Harper & Row 891p.-Illus. General (KR, 197800137).
Ramos JD, Pasqual M,
Salles LA, Chagas EA, Pio R. 2008. Receptividade do estigma e ajuste de
protocoloparagerminação in vitro de grãos de pólen de citros.
Interciência 33, 51-55.
Rapoport HF, Martins
PC. 2006. Flower quality in the olive: broadening the concept.
In Proc 2nd Intl Seminar Recent Advances Olive Industry, 21-29.
Raslan MA, Abd-Alhamid
N, Maklad MF, Laila FH. 2018. Effect of kaolin and calcium carbonate on
flowering initiation and fruit set of Kalamata and Manzanillo olive trees.
Middle East Journal of Agriculture Research 7(4), 1186-1194.
Reale L, Sgromo C,
Bonofiglio T, Orlandi F, Fornaciari M, Ferranti F, Romano B. 2006.
Reproductive biology of olive (Olea europaea L.) DOP Umbria
cultivars. Sexual Plant Reproduction 19(4), 151.
Sanz‐Cortés F,
Martínez‐Calvo J, Badenes ML, Bleiholder H, Hack H, Llacer G, Meier U. 2002.
Phenological growth stages of olive trees (Olea europaea). Annals of Applied
Biology 140(2), 151-7.
SAWCRI. 2018. Soil
and water conservation research institute, Chakwal. Annual Report, 16-18.
Shemer A, Biton I, Many
Y, Vaknin Y, Lavee S, Avidan B, Ben-Ari G. 2014. The olive cultivar
‘Picual’is an optimal pollen donor for ‘Barnea’. Scientia
Horticulturae 172, 278-284.
Stanley RG, Linskens
HF. 1974.Pollen: Biology, Biochemistry, Management, Springer, and New
York.
Tombesi A. 2013.
Advances in harvesting and pruning of olive trees. La Rivista di
Scienzadell’ Alimentazione. Journal of Food Science and Nutrition 1, 97-103.
Vuletin Selak G, Cuevas
J, Goreta Ban S, Pinillos V, Dumicic G, Perica S. 2014. The effect of
temperature on the duration of the effective pollination period in
‘Oblica’olive (Olea europaea) cultivar. Annals of applied biology 164(1), 85-94.
Vuletin Selak G, Perica
S, Goreta Ban S, Radunic M, Poljak M. 2011. Reproductive success following
self-pollination and cross-pollination of olive cultivars in
Croatia. Horticulture Science 46, 186-191.










%20in%20full.JPG)


0 comments:
Post a Comment