Meghana Kolavalli Jayanth, Paramanahally Hanumanthe Gowda Ramanjini Gowda, Neha Guleria, and Satish Kumar Kariyaiah from the different institute of the india wrote a research article about Cloning and Expression of Human GAD65 Gene in E. coli, entitled " Cloning and expression of Human glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD 65) gene in Escherichia coli " this research paper published by the International Journal of Biomolecules and Biomedicine (IJBB). an open access scholarly research journal of Biomedicine under the affiliation of the International Network for Natural Sciences | INNSpub an open access multidisciplinary research journal publisher.
Abstract
Diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by the inability of body to produce or respond to insulin a hormone required by body to burn glucose for energy. Type I Diabetes mellitus, also known as Insulin Dependent Diabetes mellitus is a most frequent chronic disease of childhood, afflicts 0.2-0.3% of human individuals due to auto immune destruction of insulin secreting pancreatic β cells. GAD65 is the major auto antigen in Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IIDM). Thus, this project is aimed at expression of GAD65 in E. coli. GAD65 gene was cloned into pET-28a bacterial expression vector and expression was studied in BL21 DE3 cells. Different parameters of induction like isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG), temperature, time interval were standardized. The recombinant clones induced with 2 μM of IPTG at 30oC for 4 h at flask level produced the protein upto 537μg/ml. Furthermore, the specificity of the purified recombinant protein was confirmed by western blot analysis using monoclonal antibodies. This work establishes a strategy in E. coli for the expression of GAD65 with optimized parameters.
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus is a
disease or disorder that is gaining importance and increasing at the alarming
rate, which is also called as hyperglycemia where the blood glucose level is
higher than the normal. According to World Health Organization, there are
mainly two principle types of diabetes; Type 1 diabetes (juvenile or insulin
dependent diabetes) and type 2 diabetes (insulin independent diabetes).Type
1diabetes an autoimmune form of diabetic disorder where the insulin producing β
cells of the pancreatic islets are destroyed. It is commonly seen in children
and the worldwide numbers of prevalent cases of T1D in children (<15 years)
have increased and the estimates indicate that there are almost 500,000
children aged under 15 years with T1D worldwide (Patterson et al., 2014). In
this type of diabetes, the autoimmune response occurs against self-antigens
which include insulin, intracellular membrane proteins such as GAD, IA2, ZnT8
transporter protein (La Torre and Lernmark, 2010; Wenzlau et al., 2009). There
is currently no cure for T1D and the only available treatment is insulin
therapy. Insulin therapy can lead to hypoglycemia if the doses are not taken
properly without monitoring blood glucose level and patients requires two or
more injections of insulin daily which is painful. (Alvarez et al., 2013).In
this regard, GAD65 a major auto antigen have much potential as an important
marker for the prediction, diagnosis and in the prevention of T1D in humans.
Autoantibodies to GAD65 are observed months to years before the clinical onset
of diabetes and are present in the sera of 70–80% of patients with T1D and this
anti-GAD 65 antibodies are now serving as an important marker for the
prediction and diagnosis of type 1 diabetes (Jayakrishnan et al., 2011; Oak et
al., 2011; Wang et al., 2012).
Glutamic acid
decarboxylase is an enzyme which is involved in the production of Gamma amino
butyric acid (GABA) by the decarboxylation of glutamate is an inhibitory
neurotransmitter in neurons and pancreatic beta cells. This GAD exists in two
major protein isoforms.
One isoform has a
molecular size of 65kDa and is termed GAD 65, while the second one, of 67kDa
size, is termed GAD67 (Towns and Pietropaolo, 2011). The GAD65 enzyme isolation
in large quantities from the human pancreatic (beta cells) tissue is
unrealistic so the expression of GAD 65 enzyme as a recombinant protein in
heterologous system is mandatory. The large scale production of GAD 65 enzyme
currently involves the use of baculovirus infected Sf9 insect cells and
methylo-trophic yeast (Mauch et al., 1993; Moody et al., 1995). However, these
expression system are technically, economically demanding and highly vulnerable
to contamination.
Number of heterologous
biopharmaceutical proteins expressed in E. coli which are at commercial level
are innumerable when compared to all other hosts system this is because of
reasons like, it is inexpensive, offers rapid culture times and the ability to
achieve high biomass and high protein yields (Assenberg et al., 2013). E. coli expression
system remain to be the first choice for laboratory investigations, scaling up
activities at commercial level and are useful benchmark for comparison among
various expression platforms. The sufficient quantity of soluble and functional
recombinant GAD 65 protein is required to carry out any molecular and
immunological studies. Poor expression of protein because of cellular toxicity
and formation of inclusion bodies are the major hindrance in recombinant
protein expression. Therefore, this study was carried out for the optimization
of different parameters to enhance GAD 65 protein expression and purification
in E. coli.
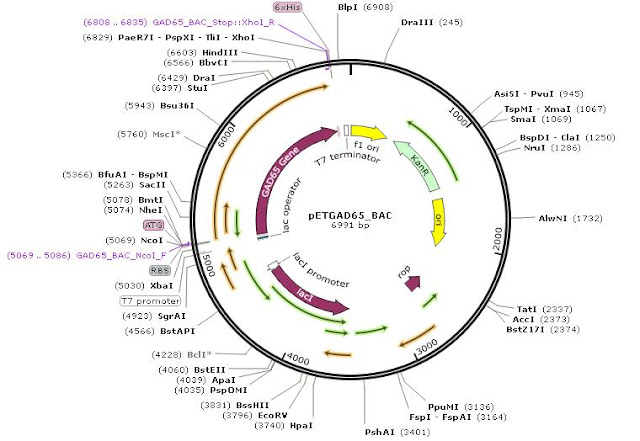
Source: Cloning and expression of Human glutamic acid decarboxylase(GAD 65) gene in Escherichia coli









%20in%20full.JPG)


0 comments:
Post a Comment